Our Verdict
UDP is faster and more efficient than TCP because it uses less data to complete the same tasks. However, TCP tracks all data packets and ensures they are delivered in the correct order, which makes it more secure and reliable. If you’re using the OpenVPN protocol, we recommend you try UDP first and switch to TCP if it doesn’t work.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) and TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) are two different types of communication protocol used to send information over the internet.
In VPN software, the OpenVPN protocol has to use either UDP or TCP to send data between your device and the VPN server. So, what’s the difference between them, and which is better for your VPN connection?
The main difference between TCP (transmission control protocol) and UDP (user datagram protocol) is that TCP is a connection-based protocol and UDP is connectionless. While TCP is more reliable, it transfers data more slowly. UDP is less reliable but works more quickly.
How do VPNs use UDP and TCP?
OpenVPN is an open-source VPN protocol used in the vast majority of secure VPN services. In many cases, users have the option to choose between OpenVPN UDP and OpenVPN TCP. In this section, we’ll explain how this decision affects your VPN’s functionality.

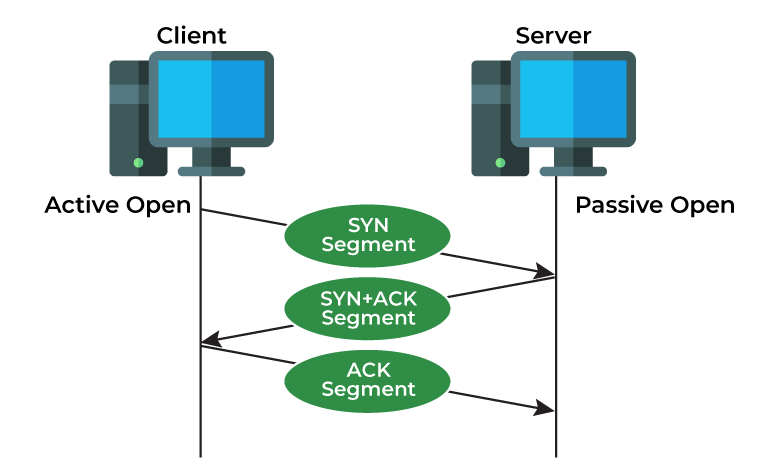
- First, imagine you’re browsing a web page without a VPN. The connection between your device and the web server will use TCP because it’s more reliable than UDP. Here’s how it works:
- When you start using a VPN, new communications are wrapped in an OpenVPN tunnel between your device and the VPN server. That tunnel connects between your device and the VPN server, and it could use either UDP or TCP.
- When you’re changing your VPN’s settings, you’re deciding which wrapper to use. So which protocol is better to use?
We’ve been testing and reviewing VPN services since 2016. We also publish VPN research and advice to help protect your internet privacy and security.